With more than 130,000 commercial and industrial grade fasteners in inventory, our wide distribution network is positioned to get you the parts you need fast. Whether we’re keeping your bins full with a Vendor Managed Inventory Program or rushing emergency replacement parts with 24-hour on-call service, you’ll know that we’ve got you covered. Our HQ’s quality system is certified to AS9120 ...
At Blue Ribbon Fastener, we specialize in providing high-quality bolts and fastening solutions tailored to meet the demands of various industries. With a commitment to precision, reliability, and durability, we ensure that our products exceed performance expectations in even the most challenging applications. Our extensive selection includes a wide range of bolts, each manufactured to exact...
Delta Fastener Corp. supplies headed fasteners from only quality manufacturers. Our huge, readily available selection includes industrial bolts, nuts, washers, screws, etc. in a wide range of metal types and grades. Check out our online catalog or give us a call today for industrial bolts and more!

P&R is a manufacturer of industrial fasteners, specialty fasteners, automotive fasteners, stainless steel fasteners, aerospace and electronic fasteners. We provide over 60 years of experience in designing quality industrial fastener products. Give us a call so we can work together.
Chicago Nut & Bolt specializes in nonstandard products such as industrial bolts, stainless steel bolts, carriage bolts, titanium bolts, mil spec bolts and alloy bolts in any quantity. We will supply any shape or size depending on your requirements. We assure quality products and on-time delivery.
More Industrial Bolt Manufacturers
Industrial Bolts: Types, Applications, and Selection Guide
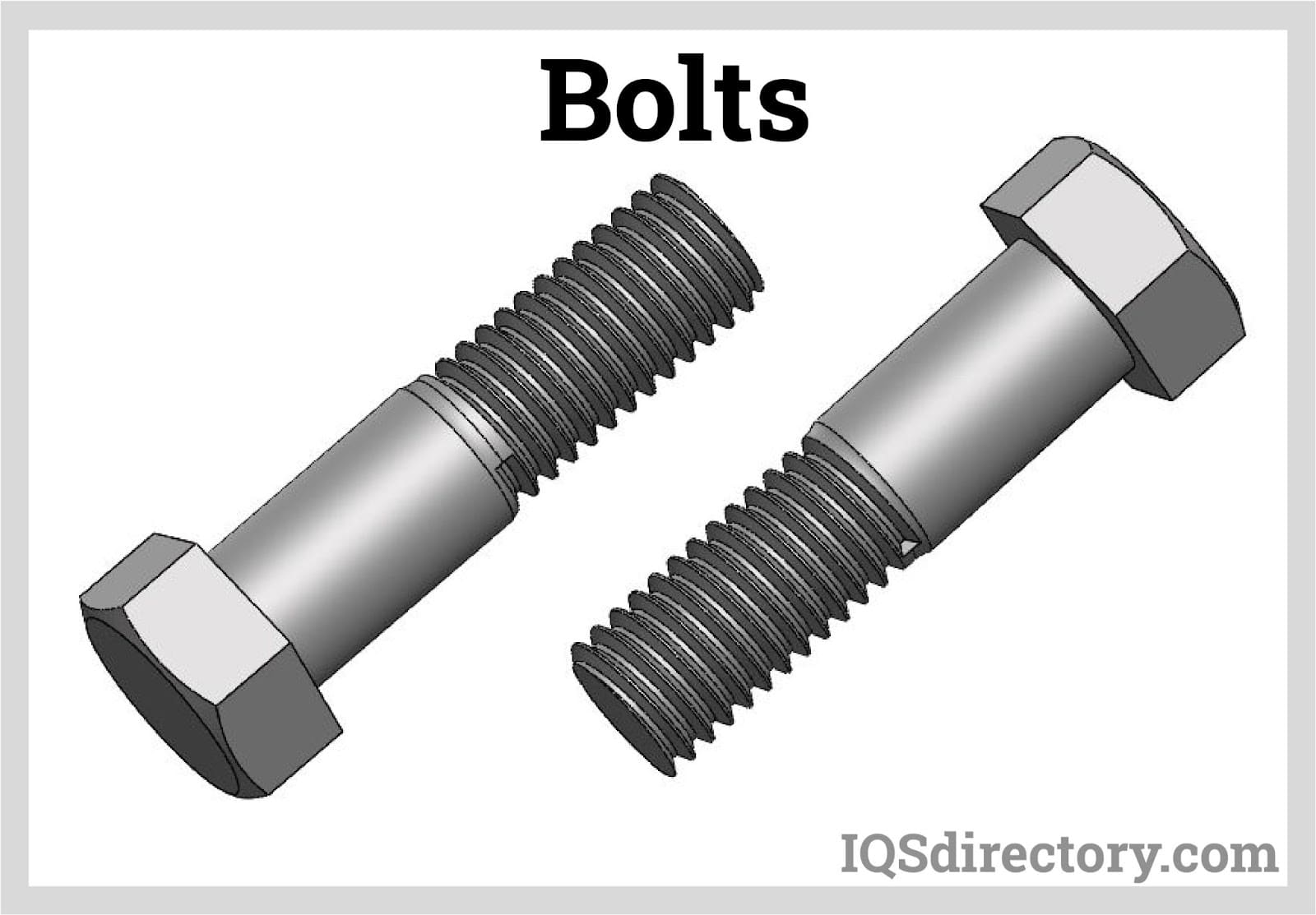
Bolts are an essential component in countless mechanical, structural, and industrial applications. Known for their versatility and strength, industrial bolts are available in a wide range of forms to suit diverse use cases. Categorized typically as hex bolts, T-head bolts, or toggle bolts, these broad groupings help buyers, engineers, and maintenance teams narrow down the specific type of bolt required for their project. With dozens of bolt types and sub-categories available, understanding bolt varieties, features, and use cases is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Overview of Bolt Types
Industrial bolts are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of modern industries. Some of the most commonly used bolt types include:
- Hex bolts: Characterized by their six-sided heads, hex bolts are widely used in construction, machinery assembly, and automotive manufacturing due to their ease of installation and compatibility with a range of tools.
- Anchor bolts: These bolts are designed to secure structural elements to concrete foundations, making them indispensable in heavy-duty construction, civil engineering, and infrastructure projects.
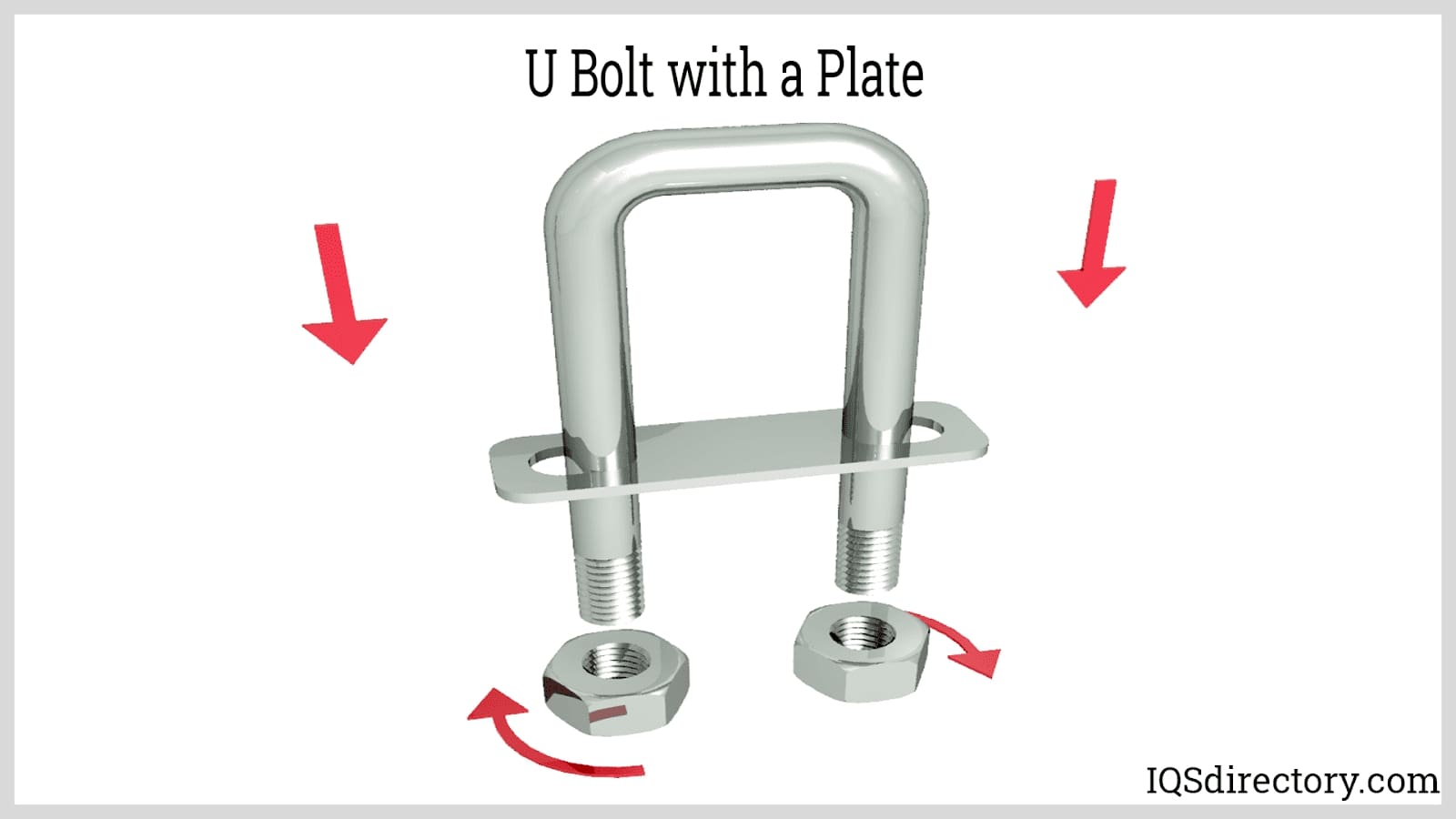
- U bolts: Shaped like the letter “U,” U bolts are ideal for securing pipes, tubes, and round objects to flat surfaces, commonly used in plumbing, automotive, and marine applications.
- J bolts: These bolts feature a J-shaped curve, providing anchorage in concrete and masonry work, particularly where a hook or loop is required for added stability.
- Eye bolts: With a circular loop at one end, eye bolts are used for lifting, rigging, and securing cables or ropes, making them prevalent in material handling, marine, and construction industries.
- Lag bolts: Featuring coarse threads and hex heads, lag bolts are ideal for fastening heavy lumber and structural supports in wood construction, decking, and outdoor projects.
- Expansion bolts: These are designed to anchor heavy loads into concrete or masonry by expanding upon installation, offering reliability in structural and architectural applications.
- Stud bolts: Threaded on both ends with a plain shaft in the middle, stud bolts are commonly used in high-pressure piping, flanges, and engine assembly where a secure, permanent joint is needed.
Industries and Applications Benefiting from Industrial Bolts
The broad selection of industrial bolts exists not only due to their efficiency and reliability but also because of the vast range of industries and use cases they serve. Bolts are fundamental in sectors such as:
- Military and Defense: High-strength bolts are critical for vehicle armor, aircraft assemblies, and secure installations where extreme performance and durability are non-negotiable.
- Aerospace: Aerospace-grade bolts are manufactured to strict tolerances, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance for aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft.
- Construction and Civil Engineering: Bolts are used in bridges, high-rise buildings, tunnels, and infrastructure, ensuring the structural integrity of large-scale projects.
- Masonry and Architectural: Specialty bolts secure stone and brick facades, curtain walls, and decorative elements in architectural projects.
- Locomotive and Rail: Bolts play a vital role in assembling and maintaining rail tracks, rolling stock, and signaling equipment.
- Mining and Petrochemical: Corrosion-resistant bolts withstand harsh environments, securing equipment in mines, refineries, and chemical plants.
- Automotive: Bolts are crucial for engine assembly, chassis construction, and safety-critical systems like brakes and suspensions.
- Nuclear: Specialized fasteners meet stringent safety standards for use in reactors, containment systems, and auxiliary structures.
Are you wondering which type of industrial bolt is best for your application? Explore our detailed guides on hex bolts, anchor bolts, and lag bolts to learn more about their unique properties, application areas, and installation methods.
Key Considerations for Selecting the Right Industrial Bolt
Choosing the optimal bolt for your project involves evaluating several critical factors that directly impact performance, safety, and cost-efficiency. These considerations include:
- Bolt Material: The majority of industrial bolts are made from high-grade steel alloys, but alternatives such as stainless steel, titanium, brass, bronze, and aluminum are available for specialized needs. Material selection should account for the operating environment, load requirements, and compatibility with joined materials.
- Bolt Dimensions: Accurately determining the required length, shank length, diameter, and threads per inch (TPI) is vital for achieving a secure, vibration-resistant connection.
- Thread Pattern: Coarse and fine thread options are available, each suited to different load and stress conditions. Fine threads provide greater tensile strength, while coarse threads are more resistant to stripping and ideal for softer materials.
- Grade and Strength: Bolt grades indicate mechanical properties such as tensile strength and hardness. For example, grade 8 bolts (identified by six radial marks on the head) are specified for demanding industrial and structural applications where superior strength is essential.
- Corrosion Resistance: Industrial bolts often face exposure to chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures. Protective coatings such as zinc plating, cadmium plating, galvanization, and specialized surface treatments can significantly extend bolt lifespan and reliability.
- Environmental Considerations: Bolts used in marine, offshore, or chemically aggressive environments must meet rigorous standards for corrosion and fatigue resistance.
Looking for guidance on how to select the right bolt for your project? Ask yourself:
- What materials am I joining, and what environmental conditions will the bolt be exposed to?
- Do I require a specific grade or certification (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for safety or compliance?
- What are the load-bearing, shear, and tensile strength requirements for my application?
- Will the bolts need to be removed frequently, or do I need a permanent, tamper-resistant solution?
Visit our Industrial Bolts Resource Hub for expert advice and in-depth articles on bolt selection, installation tips, and maintenance best practices.
Understanding Bolt Design: Components and Functionality
Industrial bolts typically consist of two to three primary components: the rod, threading, shaft, and head. While nuts and flanges are not integral bolt components, they are frequently used alongside bolts to create secure, load-distributing clamping systems. Understanding the anatomy of a bolt helps users make informed decisions regarding compatibility and performance.
- Rod: The main cylindrical body, either partially or fully threaded. The unthreaded portion, known as the shaft or shoulder, is present in some designs to accommodate shear forces and act as a bearing surface.
- Threading: Provides the mechanical grip needed to fasten components securely; thread type and pitch vary based on application and load requirements.
- Head: The top of the bolt, which can come in various shapes—hexagonal, square, flat, oval, or round—to facilitate different installation tools and torque demands.
For example, stud bolts feature threading on both ends, which is ideal for high-pressure flange connections and engine assemblies where maximum hold is required. Some bolts have tapered ends to ease installation, especially in blind or hard-to-reach locations.
Bolt head design is also a key selection criterion, with common types including binding, truss, holt, one-way, washer, and undercut heads. Each head type offers unique advantages for specific use cases, such as tamper resistance or enhanced load distribution. In addition, head markings provide critical information about bolt grade and manufacturer, which is vital for quality assurance and traceability. For instance, six radial lines denote grade 8, the minimum standard for most industrial applications.
Manufacturing Process: From Raw Material to Finished Bolt
The manufacturing of industrial bolts is a multi-step process designed to ensure consistency, performance, and safety. The process generally includes:
- Material Selection: High-strength wire rods of steel, bronze, titanium, aluminum, or brass are chosen based on the application’s mechanical and environmental demands.
- Heat Treatment: The wire rod is heated uniformly to remove rust, enhance ductility, and prepare the material for shaping. Some bolts may receive protective coatings at this stage to boost corrosion resistance.
- Cold Forging: At room temperature, the metal is forced through dies under high pressure to achieve the desired cylindrical shape and dimensional accuracy.
- Cutting and Heading: The shaped rod is cut to the required length, and a secondary die forms the bolt head if necessary.
- Thread Rolling: High-pressure rollers are used to imprint the thread pattern onto the bolt. This cold working process enhances surface hardness and fatigue resistance.
- Finishing: Secondary treatments such as additional coatings, quality control inspections, and packaging complete the manufacturing cycle.
The resulting bolts are ready for deployment across a wide array of industrial, structural, and mechanical applications.
Industrial Bolt Coatings and Finishes: Enhancing Durability
Bolts are often subject to challenging environments—exposure to moisture, chemicals, salt spray, and temperature fluctuations. To address these challenges, manufacturers use specialized coatings and finishes such as:
- Zinc Plating: Provides a cost-effective barrier against corrosion, making it suitable for general-purpose and low-moisture environments.
- Cadmium Plating: Offers superior corrosion and galvanic protection, often specified for aerospace and marine fasteners.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Delivers a thick, durable zinc layer ideal for outdoor, marine, and infrastructure applications.
- Phosphate Coating: Enhances lubricity and corrosion resistance, commonly used for automotive and machinery bolts.
- Specialty Coatings: PTFE, epoxy, and ceramic coatings are available for highly corrosive or extreme temperature environments.
Curious about which coating is best for your project? Discover our guide on Industrial Bolt Coatings and Treatments for a detailed comparison of options by industry and application.
How to Install and Maintain Industrial Bolts for Maximum Performance
Proper installation and routine maintenance are crucial to ensuring the safety, reliability, and longevity of bolted joints. Here are some fundamental tips:
- Torque Specifications: Always follow manufacturer-recommended torque values to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening, both of which can compromise joint integrity.
- Use of Washers and Locking Devices: Washers, lock nuts, and thread-locking compounds can help prevent loosening due to vibration and dynamic loads.
- Inspection Schedules: Regularly inspect bolts for signs of corrosion, fatigue, and wear. Replace any bolts showing deformation, cracks, or excessive thread wear.
- Lubrication: Applying the correct lubricant can reduce friction during installation and protect against galling or seizing, especially for stainless steel bolts.
- Environmental Protection: For outdoor or harsh environments, select bolts with appropriate coatings and consider sealing or covering exposed fasteners.
Want to learn more about bolt installation best practices? Read our in-depth article on Industrial Bolt Installation Tips for step-by-step guidance and troubleshooting advice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Industrial Bolts
- What is the difference between a bolt and a screw? While both are threaded fasteners, bolts are typically used with nuts to clamp components, whereas screws are often threaded directly into materials.
- How do I determine the right bolt size for my project? Consider the thickness of materials, required clamping force, and recommended industry standards. Consult manufacturer charts or use online bolt sizing calculators for guidance.
- What are the most durable bolts for outdoor use? Stainless steel, hot-dip galvanized, or coated bolts provide superior resistance to weathering, corrosion, and UV exposure.
- Can I reuse industrial bolts? In many cases, bolts can be reused if they show no signs of damage or fatigue, but high-stress or safety-critical applications may require new fasteners for each installation.
- Where can I buy industrial bolts in bulk? Leading suppliers and manufacturers offer bulk purchasing options with custom specifications. Find trusted industrial bolt suppliers here.
Industrial Bolts: Key Benefits and Decision Factors
Industrial bolts offer a host of advantages that make them the fastening solution of choice across many industries:
- High Load Capacity: Engineered for maximum strength, bolts can handle significant shear and tensile forces.
- Versatile Applications: With countless sizes, shapes, and materials, bolts provide solutions for virtually any connection challenge.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Bolted joints can be assembled, adjusted, or disassembled using standard tools, simplifying repairs and modifications.
- Reliability and Safety: Quality manufacturing standards and traceability ensure confidence in performance-critical applications.
- Customization: Manufacturers offer custom bolt solutions, including special alloys, coatings, head styles, and thread patterns for unique project needs.
Evaluating which bolt is right for your needs? Consider factors such as required strength, corrosion resistance, industry certifications, and total cost of ownership. Request a custom quote today to get started with your project.
Explore More: Related Resources and Guides
- Hex Bolts: Features, Applications, and Manufacturers
- Anchor Bolts: Types and Use Cases
- Lag Bolts: Selection, Installation, and Sourcing
- Stud Bolts: High-Pressure Applications
- More Industrial Bolt Resources and Supplier Listings
Whether you are sourcing bolts for a major infrastructure project, specifying fasteners for OEM manufacturing, or seeking the best bolt materials for harsh environments, our comprehensive resource library is designed to support your buying journey, technical research, and application needs.
Have specific questions or need technical assistance? Contact our bolt specialists for personalized recommendations and engineering support.





 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services