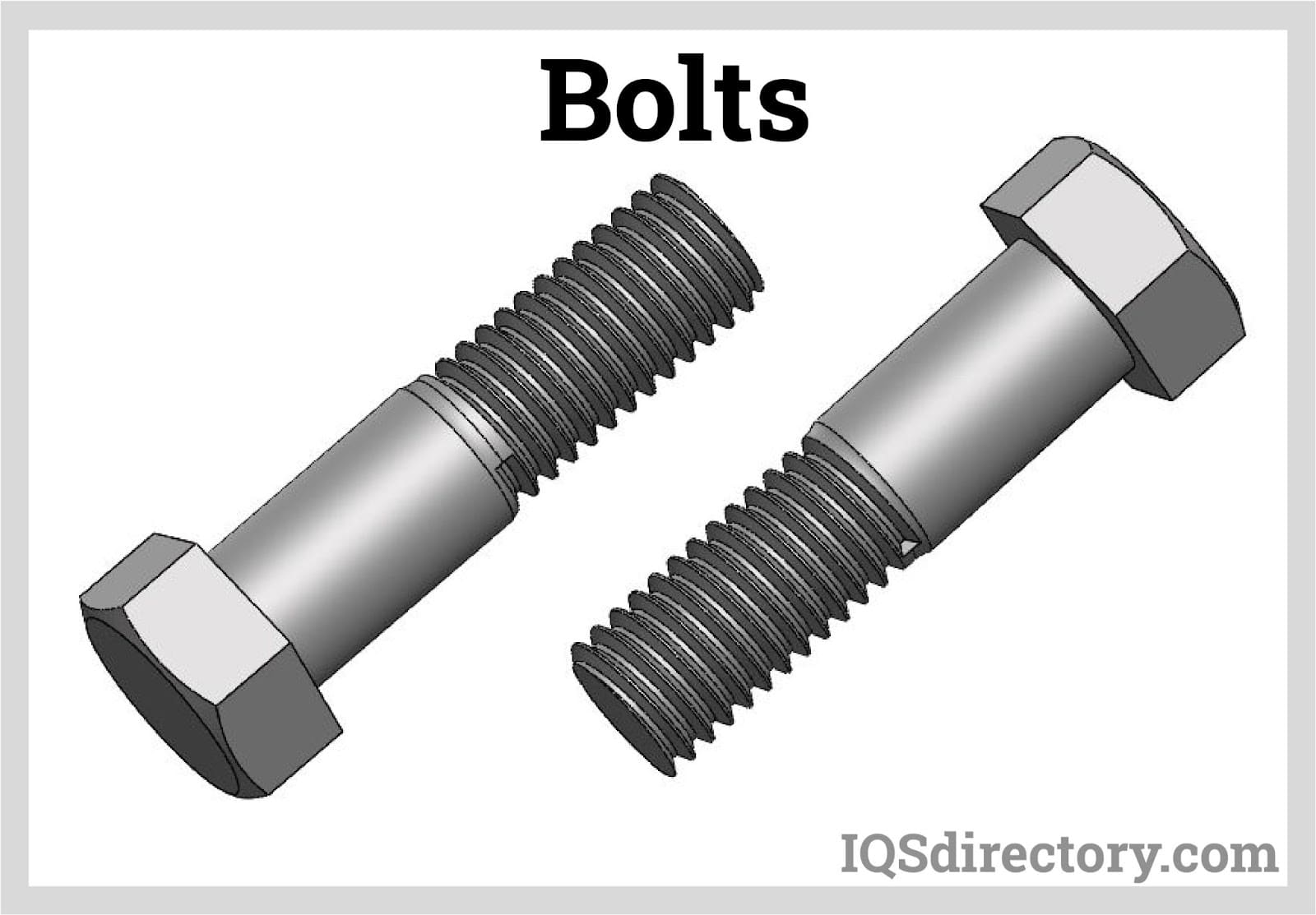
Bolts are a common and essential part of modern construction and manufacturing. They are used to securely join two or more objects together and are designed to withstand high-stress loads. Bolts have been around for centuries, with the earliest known bolts dating back to ancient Greece. Over time, bolts have evolved to become an essential part of modern construction and manufacturing. Bolts come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications. Read More…
With more than 130,000 commercial and industrial grade fasteners in inventory, our wide distribution network is positioned to get you the parts you need fast. Whether we’re keeping your bins full with a Vendor Managed Inventory Program or rushing emergency replacement parts with 24-hour on-call service, you’ll know that we’ve got you covered. Our HQ’s quality system is certified to AS9120 ...
At Blue Ribbon Fastener, we specialize in providing high-quality bolts and fastening solutions tailored to meet the demands of various industries. With a commitment to precision, reliability, and durability, we ensure that our products exceed performance expectations in even the most challenging applications. Our extensive selection includes a wide range of bolts, each manufactured to exact...
Delta Fastener Corp. supplies headed fasteners from only quality manufacturers. Our huge, readily available selection includes industrial bolts, nuts, washers, screws, etc. in a wide range of metal types and grades. Check out our online catalog or give us a call today for industrial bolts and more!

P&R is a manufacturer of industrial fasteners, specialty fasteners, automotive fasteners, stainless steel fasteners, aerospace and electronic fasteners. We provide over 60 years of experience in designing quality industrial fastener products. Give us a call so we can work together.
Chicago Nut & Bolt specializes in nonstandard products such as industrial bolts, stainless steel bolts, carriage bolts, titanium bolts, mil spec bolts and alloy bolts in any quantity. We will supply any shape or size depending on your requirements. We assure quality products and on-time delivery.
More Industrial Bolt Manufacturers
Bolts are a fundamental component in modern construction, industrial assembly, and manufacturing, serving the crucial role of securely joining two or more objects together. As one of the primary fastener types used worldwide, bolts are engineered to withstand high-stress loads and provide durable, long-lasting connections in a wide variety of structural and mechanical applications. Their importance in both heavy-duty and precision engineering cannot be overstated—bolts have been integral to construction for centuries, with their earliest use tracing back to ancient Greece and Rome for architectural and military purposes. Over time, bolt design and manufacturing processes have evolved to keep pace with the ever-increasing demands of modern engineering, making bolts indispensable in nearly every industry from infrastructure and machinery to transportation and electronics. Available in a wide range of shapes, sizes, threads, and finishes, each type of bolt is engineered for a specific use case to ensure optimal performance, safety, and reliability.
Materials Used for Bolts
When selecting bolts for your project, choosing the right material is critical to achieving the desired performance and longevity. Bolts can be manufactured from a wide range of materials, each offering unique advantages for different environments and load requirements. The most common materials include:
- Steel Bolts: The most widely used fasteners, carbon steel bolts offer high strength and durability for general construction, machinery, and automotive applications. They are available in various grades—such as Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8—each with specific tensile strength ratings. Steel bolts may be zinc-plated, galvanized, or coated for additional corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel Bolts: Favored for their corrosion resistance, stainless steel bolts are ideal for outdoor, marine, and chemical environments. Grades such as 304 and 316 stainless steel provide excellent resistance to rust and oxidation, making them suitable for harsh and humid conditions.
- Titanium Bolts: Titanium fasteners combine high strength-to-weight ratio with excellent corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in aerospace, motorsports, and medical devices where both performance and weight savings are essential.
- Brass Bolts: Brass bolts are valued for their electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion in water, making them a preferred option for electrical, plumbing, and marine applications.
- Alloy Steel Bolts: These are engineered for high-stress applications and extreme environments, offering superior strength and toughness.
- Other Specialty Materials: In highly specialized industries, bolts may be manufactured from bronze, aluminum, Inconel, Monel, or plastic composites to meet unique performance criteria.
Choosing the optimal bolt material depends on variables such as mechanical strength requirements, exposure to corrosive environments, temperature extremes, and the need for electrical insulation or conductivity. If you’re wondering, “Which bolt material is best for my application?”—explore our industrial bolt manufacturer directory for expert guidance and custom solutions tailored to your needs.
Design and Application Differences of Bolts
Bolt design is highly specialized, with each type engineered for a distinct application or installation method. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right fastener for your project. Common bolt types include:
- Anchor Bolts: Used to secure structural elements to concrete foundations, anchor bolts are commonly found in building construction, bridges, and heavy machinery installations.
- Carriage Bolts: Featuring a smooth, rounded head and square neck, carriage bolts are ideal for wood-to-wood or wood-to-metal connections, providing a finished appearance and resistance to turning during tightening.
- Expansion Bolts: Designed to anchor objects into masonry or concrete, expansion bolts expand upon tightening to create a strong hold in brittle materials.
- Eye Bolts: These bolts have a looped head, making them suitable for lifting and rigging applications or as anchor points for cables and ropes.
- Hex Bolts: Recognized by their six-sided heads, hex bolts are among the most versatile and commonly used in general construction, machine assembly, and automotive repair.
- Industrial Bolts: A broad category encompassing heavy-duty fasteners for manufacturing, structural steelwork, and equipment assembly.
- J Bolts: Shaped like the letter “J,” these are embedded in concrete and used for securing structural columns or machinery.
- Lag Bolts (Lag Screws): Large wood screws with hex heads, lag bolts are used for heavy timber construction and deck building.
- Metric Bolts: Manufactured to ISO metric thread standards, metric bolts are essential for international machinery, automotive, and electronics assembly.
- Shoulder Bolts (Stripper Bolts): With a smooth, unthreaded shoulder, these bolts are used as pivot points or for applications requiring precise movement or alignment, such as robotics and automation.
- Stud Bolts: Threaded at both ends, stud bolts are commonly used in flange connections in piping, pressure vessels, and heavy equipment.
- Thru-Bolts: Designed to pass completely through the connected materials, allowing for secure fastening with nuts and washers on both sides.
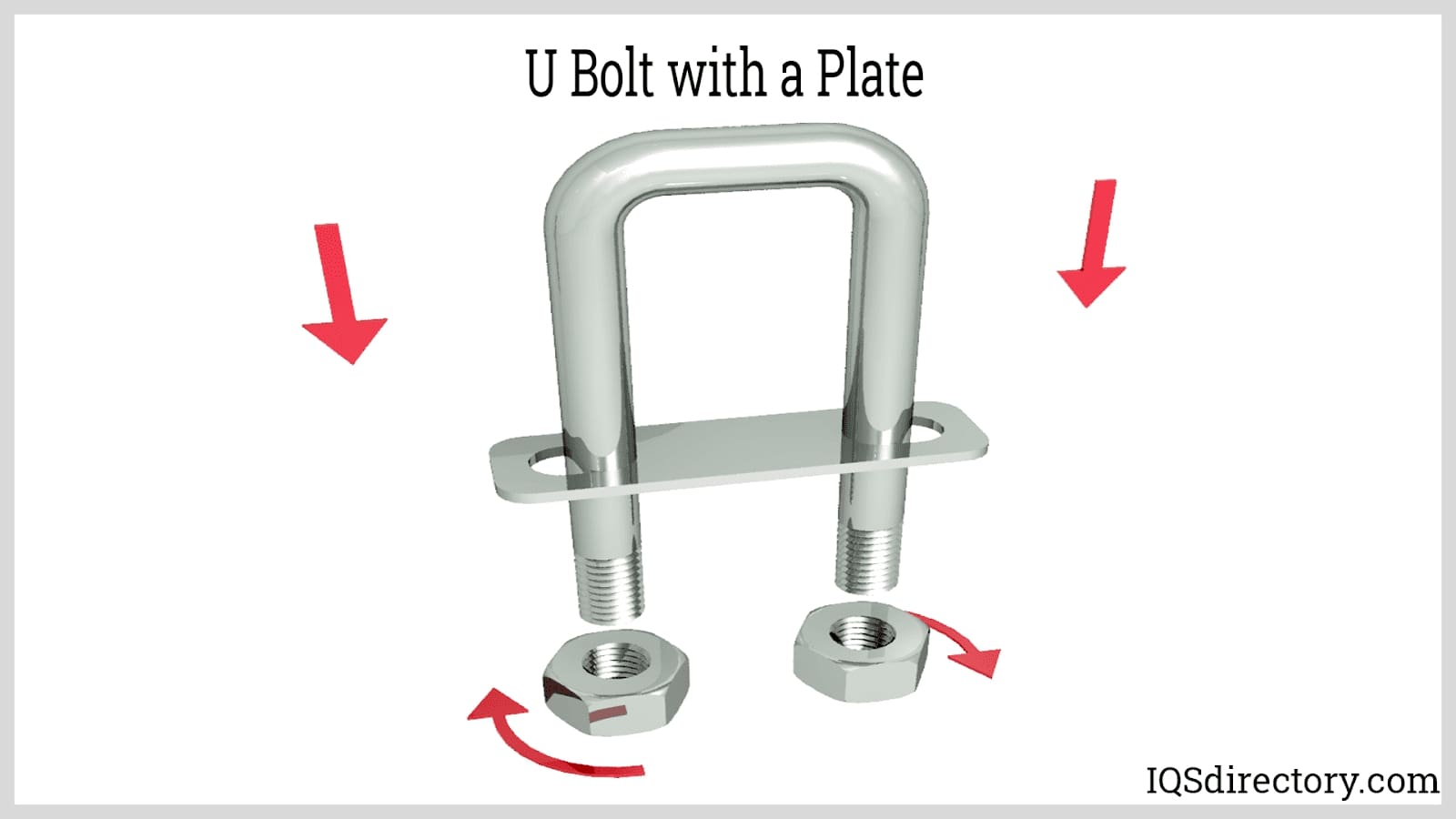
- U Bolts: U-shaped bolts used to secure pipes, tubes, or round objects to a surface or frame.
Each of these bolt types is engineered to meet specific strength, installation, and environmental requirements. Not sure which bolt is best for your application? Ask yourself: “What are the load, environmental, and assembly considerations for my project?” Our industrial bolt supplier directory can connect you with manufacturers offering custom and standard solutions for every scenario.
Factors When Choosing Bolts
When sourcing bolts for construction, industrial, or commercial projects, several important factors should guide your decision. Addressing these considerations will help optimize safety, performance, and cost efficiency:
- Load Requirements: Assess the maximum tensile, shear, and fatigue loads expected in your application. Choose a bolt grade and material with sufficient strength to handle these forces.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider exposure to moisture, chemicals, saltwater, UV radiation, or temperature extremes. Select corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or coated steel for harsh environments.
- Thread Type and Size: Ensure compatibility with mating nuts or tapped holes by matching thread pitch, diameter, and length. Both metric and imperial thread standards are available depending on regional or industry requirements.
- Installation Method: Determine accessibility and available tools for tightening or loosening bolts. Some applications may require pre-installed anchors, while others favor easy removal and reusability.
- Regulatory Standards: Projects in critical industries (aerospace, automotive, construction) may require fasteners certified to ASTM, ISO, DIN, SAE, or other standards for quality assurance and traceability.
- Cost Considerations: Balance the upfront cost of materials and coatings with long-term durability, maintenance, and replacement frequency.
Bolts are renowned for their reliability and strength, but they do have certain limitations. For example, bolts can corrode over time if exposed to harsh environments without adequate protection, potentially resulting in joint failure. Additionally, improper installation—such as over-tightening or using the wrong grade—can compromise structural integrity. These challenges can be mitigated by selecting the appropriate bolt material, design, and protective finish, as well as adhering to recommended torque specifications and best practices. Curious about how to prevent bolt failures? Read our guide on bolt failure prevention strategies.
Benefits Provided by Bolts
Bolts offer a multitude of benefits across industries and applications. Here’s why bolts continue to be the fastening solution of choice for engineers, architects, and manufacturers:
- Strength and Stability: Bolts create a secure and stable connection between multiple objects, making them ideal for applications requiring high strength. Their robust design enables them to endure significant tension and compression without breaking or deforming, supporting heavy loads and resisting loosening under vibration.
- Easy to Install: Bolts are relatively easy to install, requiring only basic hand or power tools for secure tightening. This simplicity reduces installation time and labor costs, making bolts popular for both DIY projects and large-scale construction alike.
- Versatility: Available in a vast array of sizes, shapes, materials, and threading options, bolts are a versatile fastening solution suitable for a wide range of applications. Their design allows for adjustability during assembly and disassembly, which is particularly useful for projects requiring precise alignment or future modifications.
- Cost-Effective: Bolts are a cost-effective fastening option, particularly when compared to alternatives like welding, adhesives, or riveting. They require less specialized equipment and can often be reused, leading to significant savings over a project’s lifecycle—especially in scenarios where disassembly and reassembly are necessary.
- Corrosion Resistance: Many bolt materials, such as stainless steel, brass, and coated carbon steel, offer excellent resistance to corrosion, making bolts an ideal choice for outdoor, marine, and chemical applications.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Bolts can be customized with various finishes (such as black oxide, chrome, or polished stainless) to match the aesthetic requirements of an application. This is important in architectural, furniture, and consumer product design where appearance matters.
- Reusability: Unlike permanent joining methods, bolts allow for easy removal and reinstallation, supporting maintenance, upgrades, and repairs without damaging the components being joined.
Applications of Bolts
Bolts are essential fasteners used in a diverse range of industries and applications. Their adaptability and strength make them the preferred choice for both temporary and permanent assemblies. Key application areas include:
- Construction: In the construction industry, bolts play a critical role in joining steel beams, concrete foundations, and pre-fabricated elements. Structural bolts, anchor bolts, and heavy hex bolts are frequently used in steel framing, bridge construction, and building infrastructure.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Automotive bolts are used to secure a wide variety of vehicle components, such as engines, transmissions, axles, chassis, suspension systems, wheels, and more. High-performance automotive bolts must meet rigorous safety and quality standards to ensure the integrity and reliability of vehicles in operation.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies heavily on precision-engineered bolts to secure critical components, airframes, and engine assemblies. Aerospace bolts are often manufactured from exotic materials like titanium or high-strength alloys and are subject to strict quality control and certification standards.
- Manufacturing Machinery: Bolts are integral in manufacturing machinery assembly, where they connect moving parts, secure housings, and mount equipment to floors or workbenches. In electrical and electronic equipment fabrication, bolts are used to fasten components to enclosures or chassis, sometimes requiring non-conductive or insulated bolts to prevent shorts.
- Marine: In the marine industry, bolts secure vital components of ships, such as engines, hull fittings, and propeller assemblies. Marine-grade bolts are made from materials like stainless steel, bronze, or Monel to withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater and moisture.
- Agriculture: Bolts are used extensively in agricultural machinery, fastening components on tractors, planters, harvesters, and irrigation systems. They also anchor structures like grain bins, silos, and fencing to ensure stability in variable environmental conditions.
- Furniture Manufacturing: In furniture manufacturing, bolts are used to join frames, legs, and supports, providing both stability and the ability to disassemble for transport or storage. Specialty bolts for furniture include connector bolts and barrel nuts, which offer hidden or decorative fastening.
- Sporting Equipment: Sporting goods manufacturers rely on bolts to assemble bicycles, skateboards, snowboards, exercise equipment, and more. The right bolt ensures safety, durability, and user adjustability.
- Medical Equipment: In medical device and equipment manufacturing, bolts are used to secure assemblies and enclosures. Materials must withstand frequent sterilization, exposure to chemicals, and in some cases, biocompatibility requirements for implants or surgical tools.
- Energy Sector: Bolts are essential for assembling wind turbines, solar panel racks, oil rigs, and power transmission infrastructure, where they must endure vibration, corrosion, and extreme loads.
- Railways and Infrastructure: Railroads use specialized bolts to fasten rails, join structural members, and assemble signaling equipment, demanding high strength and resistance to fatigue.
Do you need bolts for a specific industry or project? Browse our comprehensive supplier listings to find the ideal manufacturer for your requirements.
Decision Factors: How to Choose the Right Bolt
With so many bolt types, materials, and finishes available, making the right selection can feel overwhelming. Consider these key decision factors before making your purchase:
- Application Environment: Will the bolt be exposed to moisture, chemicals, high temperatures, or mechanical vibration? Choose a material and coating that matches the environment to ensure longevity and performance.
- Mechanical Loads: Determine the static and dynamic forces the bolt will experience. Calculate required tensile and shear strengths and select a bolt grade accordingly.
- Size and Thread Compatibility: Verify required length, diameter, and thread type (UNC, UNF, metric, etc.) for proper fit and performance.
- Regulatory and Safety Standards: Confirm that your project requires compliance with specific standards (ASTM, ISO, SAE, DIN). Look for manufacturers who provide traceability and certification.
- Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Consider whether the bolt will need to be removed for service, and whether there are space or accessibility constraints for tools.
- Supplier Reputation and Support: Work with a reputable bolt manufacturer or distributor who can provide technical support, quality assurance, and on-time delivery.
- Cost and Lifecycle Value: Don’t simply choose the lowest price—factor in corrosion resistance, reusability, and potential maintenance or replacement costs over time.
Have more questions? Try searching:
- “How do I select the correct bolt grade for heavy machinery?”
- “What are the best corrosion-resistant bolts for marine use?”
- “Which bolt types are suitable for high-vibration environments?”
- “Where can I order custom-size bolts for a unique application?”
Choosing The Right Bolt Supplier
To achieve the best results when purchasing bolts, it’s essential to compare multiple suppliers to ensure quality, pricing, and reliability. Our industrial bolt manufacturer directory streamlines your search. Each supplier’s profile page highlights their expertise, product range, certifications, and capabilities, along with a convenient contact form for direct inquiries or quote requests. Utilize our patented website previewer to quickly assess each company’s specialties in fastener manufacturing, supply chain capacity, and value-added services such as custom engineering or kitting. Finally, use our straightforward RFQ (Request for Quote) form to communicate with several bolt companies simultaneously—saving you time and ensuring you receive competitive bids for your project.
When evaluating bolt suppliers, consider factors like technical support, lead times, shipping options, minimum order quantities, and after-sales service. Leading suppliers may also offer inventory management, just-in-time delivery, and engineering consultation to optimize your fastening solution.
Conclusion: Bolts as the Backbone of Modern Industry
Bolts remain at the heart of industrial progress, providing the strength, reliability, and flexibility required in today’s demanding environments. Whether you’re building skyscrapers, manufacturing precision equipment, or maintaining critical infrastructure, the right bolts ensure the safety and longevity of your projects. Understanding bolt types, materials, standards, and sourcing strategies empowers you to make informed decisions and achieve optimal results. Ready to take the next step? Explore our directory of trusted industrial bolt manufacturers and request quotes today.
What are bolts and why are they important in modern industry?
Bolts are a fundamental type of fastener used to securely join two or more objects. Engineered for strength and durability, they play a crucial role in construction, manufacturing, machinery, transportation, and many other fields, providing reliable connections that endure high stress and vibration. Bolts have been essential since ancient times, evolving to meet the complex demands of today’s engineering projects.
What materials are commonly used to manufacture bolts?
The most common materials for bolts include carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium, brass, alloy steel, and specialty options like bronze, aluminum, Inconel, Monel, or plastics. Each material offers unique benefits for mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, and suitability for various environments and applications.
What are the different types of bolts and their applications?
There are many specialized bolt types, such as anchor bolts for concrete foundations, carriage bolts for wood connections, expansion bolts for masonry, eye bolts for lifting, hex bolts for general assembly, J bolts for structural embedding, lag bolts for timber, metric bolts for international standards, shoulder bolts for precision alignment, stud bolts for flange connections, thru-bolts for pass-through assemblies, and U bolts for securing pipes and tubes. Each type is engineered for specific installation and performance needs.
What factors should I consider when choosing bolts for my project?
Key factors in bolt selection include load requirements, environmental conditions, thread type and size, installation method, compliance with regulatory standards, and cost considerations. Evaluating these aspects ensures optimal performance, safety, and value throughout the lifecycle of your project.
What are the main benefits of using bolts over other fastening methods?
Bolts provide strong, stable connections, are easy to install and remove, offer versatility in size and material, and support cost-effective, reusable, and corrosion-resistant solutions. They can also be finished for appearance and allow for precise assembly or disassembly when maintenance is needed.
In which industries and applications are bolts most commonly used?
Bolts are widely used in construction (joining steel and concrete), automotive (securing components), aerospace (airframes and engines), manufacturing machinery, marine (shipbuilding and equipment), agriculture, furniture, sporting equipment, medical devices, energy sector (wind turbines, power infrastructure), and railway systems. Their adaptability makes them indispensable across these varied applications.
How can I choose the right bolt supplier for my needs?
When selecting a bolt supplier, compare expertise, product range, certifications, technical support, lead times, shipping options, pricing, and after-sales service. Utilize supplier directories to access profiles and request quotes from multiple companies to ensure you get reliable, high-quality fasteners at competitive prices.



 Bolts
Bolts Fasteners
Fasteners Gas Spring
Gas Spring Handles
Handles Hinges
Hinges Latches
Latches Locks
Locks WIre Hooks
WIre Hooks Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services